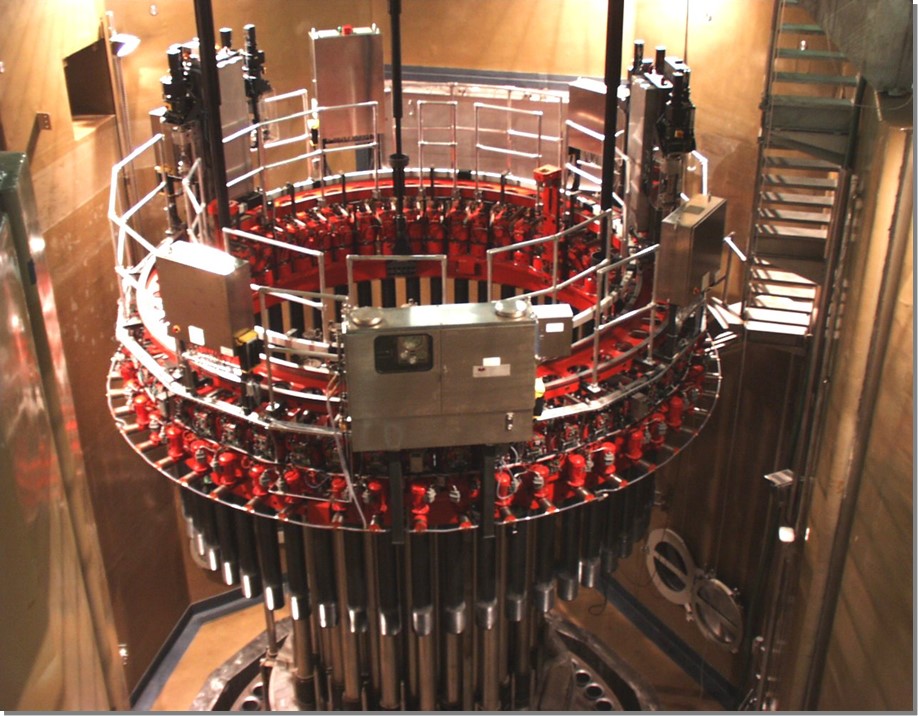
Mutli Stud Tensioner
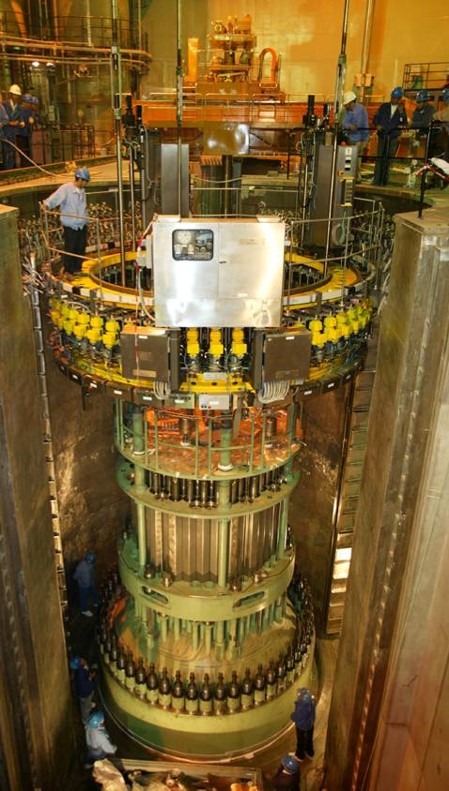

Multi Stud Tensioner for PWR (Pressurized Water Reactor)
The reactor pressure vessel in nuclear power plants needs to be maintained at intervals of approximately twelve to eighteen months for replacing spent fuel elements by new ones, and to perform the inspections and tests stipulated by the government authorities. The reactor consists of the bottom part, the so-called reactor vessel, and the top part, the reactor cover. Up to 60 studs and nuts distributed at equal intervals on the circumference of the vessel join and press these two parts together. Generally, one of the tasks during the outage work is under special focus; it is the de-tensioning and the re-tensioning of the RPV head.
In addition to this work is the RPV stud spin in and out of the Reactor Vessel Blind Holes. Additional mobilization work for the RV Stud Turning equipment and intermediate stud storage racks has to be considered by the containment crane. Due to the amount of work required during a reactor overhaul on a PWR, it was necessary to design a machine that could perform this work without additional using of the containment crane. It is also important to mention that the critical MST components for the tensioning process are redundantly designed.
The Multi Stud Tensioners for PWRs are considering that the RPV Stud turning, handling and transportation is a fundamental part of the RPV head maintenance and minimizing the number of operating staff in the reactor cavity. Therefore, the ALARP aspect is fully considered in design and in reducing the personnel exposure significantly.
Therefore, a Multi Stud Tensioner machine equipped with Double Stud or Single Stud Turning Robots was designed for the de-/ tensioning of a Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV).
The MST is not only used for de-/ tensioning the RPV bolt, also other attached components, e.g. the Double Stud Turning Robots (DSTR), in order to remove and install the RPV studs. The RPV Stud turning needs no additional mobilization or transport time for the Stud Turning equipment and Stud Racks for intermediate storage because this equipment is already attached to the MST.
A platform is installed onto the MST support ring and two DSTRs are operating automatically, separately and independently from each other.
The DSTRs are removing or installing the RV studs through the RPV cover into the blind hole of the Reactor vessel. The whole RV stud turning process is monitored, logged and recorded during the operation.
The MST is designed in such a way that the RPV Studs with nuts and washers are taken over into the machine and secured for transport. A typical operating time for detensioning or tensioning the Reactor Pressure Vessel is between 45 minutes and 60 minutes.
For the RPV stud installation or removal 1h 30 to 2 hours operating time is to be considered as typical.
After RPV detensioning and Stud removal the MST with the RPV studs is transported from the reactor cover to the storage stand.
The RPV cover is now ready to be lifted off and one can proceed with the further sequences in the reactor maintenance. The operating time of the MST install until the machine to lift off is between 2 and 3 hours.
Multi Stud Tensioner for BWR (Boiling Water Reactor)
The detensioning and tensioning work of a BWR Multi Stud Tensioner is one of the main tasks during the plant outages of a BWR. The concept for a boiling water Multi Stud Tensioner is comparable to a pressurized water reactor Multi Stud Tensioner. The tensioning technology principle is the same. The difference is that in accordance to the plant procedures only a certain amount of the RPV studs has to be removed for further material investigations. It means the main task and the focus is the detensioning and tensioning of RPV studs.
Therefore, the Multi Stud Tensioner is used for detensioning / tensioning of all reactor studs at the same time, with the same tensioning force. During the detensioning or tensioning process, digital measurement gauges monitor and record the elongation at each RPV stud.
All elongation measurement data and pressure data of the tensioning process are logged and memorized.
The MST also has another important function that saves a lot of time, radiation exposure dose, and effort for the operator and finally reduces the outage cost.
With this function, all RPV nuts are turned off simultaneously and transferred to the support ring of the MST with an integrated support device in the process of RPV detensioning. In between the detensioning and tensioning process the RPV nuts are easily unloaded and the inner threads are easily cleaned.
For the tensioning process, all RPV Nuts are transported with the integrated support device to the RPV and turned onto the RPV studs.
A typical operating time for detensioning or tensioning the Reactor Pressure Vessel is between 100 minutes and 150 minutes. It includes the 100 % automatically RPV nut turning and tensioning or detensioning the RPV studs.
The RPV studs (most of the time a fourth part of the Reactor studs) have to be turned by a separate Stud Turning Robot. The RV Stud Turning Robot has an own driving mechanism for moving forward from one RV stud to the next. During the whole Stud turning and positioning procedure the RV Stud Turning Robot is secured to prevent from falling down.